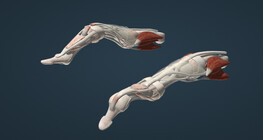
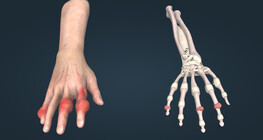
In rheumatoid arthritis, two of the most common deformities of the fingers are boutonnière and swan-neck deformity.
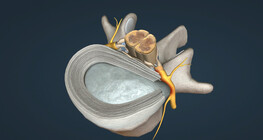
This animation shows the different types of intervertebral disc herniation.
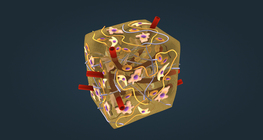
Connective tissues include loose and dense connective tissues, adipose tissue, blood, tendon and bone tissue.
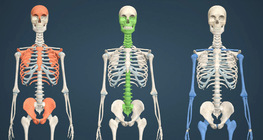
This scene explains the structure and functions of the bones.
Types of connective tissue in the musculoskeletal system
Osteoarthritis encompasses a range of joint diseases, with osteoarthritis being the most common degenerative type. It primarily involves the gradual breakdown of hyaline cartilage, which leads to subsequent changes in the subchondral bone and potential damage to periarticular structures, leading to decreased muscle function around the joint.
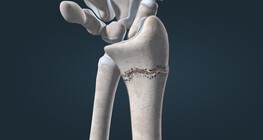
Inflammation in the early stages of rheumatoid arthritis often involves the wrist, potentially leading to deformities at an early stage if left untreated.
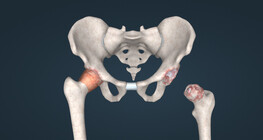
Gout, or arthritis urica, is a systemic disease belonging to the family of crystalline arthropathies, in which genetic background and environmental factors play a role.
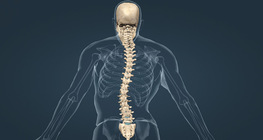
Scoliosis is a sideways curve of the spine. The curve can occur on either side of the spine and in different spine segments.
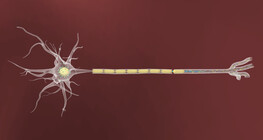
The severity of peripheral nerve injuries can be assessed using Seddon's classification.
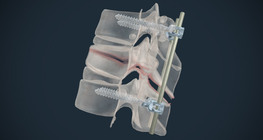
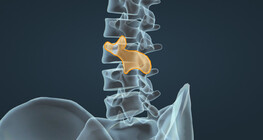
The surgical procedure can relieve the pressure on the fractured vertebral body or restore the vertebral body to its original shape.
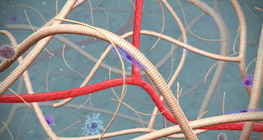
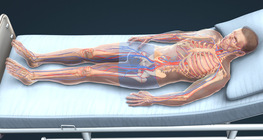
A blood clot that forms in the deep veins of the lower limbs can cause a fatal pulmonary embolism if it enters the lungs.
This application demonstrates the bones, joints, ligaments, and additional joint structures of the human body.
The Scottie dog sign indicates the typical appearance of the lumbar spine as observed in oblique radiographic projections.
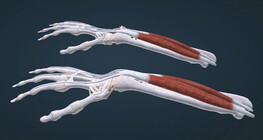
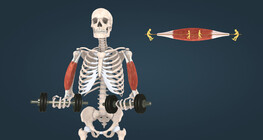
Muscle contractions can be dynamic, causing joint movement, or static, producing force without movement.
Ankylosing spondylitis is an inflammatory condition belonging to the spondyloarthritides group and is primarily associated with axial involvement. The disease mainly causes inflammation of the entheses (the points where ligaments and tendons attach to bone), but many other organ systems may also be affected.
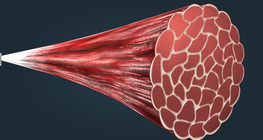
This animation demonstrates the fine molecular structure and mechanism of muscles.
Bone remodelling occurs in response to load changes, a process during which the structure of bones is adjusted constantly and dynamically.
Bone repair occurs through direct intramembranous healing or indirect healing with endochondral ossification.